The United States represents a beacon of opportunity for individuals and families around the world. The country can bring economic prosperity, world-class education, and familial legacy to its inhabitants. The stable democratic society continues to draw millions who dream of building a new life on American soil. One of the most direct and well-established routes for foreign investors is the EB-5 immigrant investor program. This program offers a unique opportunity to obtain a U.S. green card in exchange for a significant investment in a U.S. commercial enterprise. For F-1 students and H-1B professionals, this pathway provides unprecedented stability.
This comprehensive guide will dive deep into the intricacies of the EB-5 program, explore its rich history as well as any recent legislative changes and the various investment options available to prospective immigrants.
What is the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program?
The EB-5 program was created by the United States Congress as part of the Immigration Act of 1990. The program was designed to stimulate the U.S. economy through job creation and to attract foreign capital. In return for their investment, foreign nationals, their spouses and unmarried children under the age of 21 became eligible to apply for LPR (lawful permanent residence) in the United States.
The program has undergone several modifications since its inception with the most significant changes occurring in 2022 with the Reform and Integrity Act introduction.
The Evolution of the EB-5 Program: Historical Perspective
Understanding the history of the EB-5 program provides valuable context for its current structure and requirements. Below are the milestones of the EB-5 program's history:
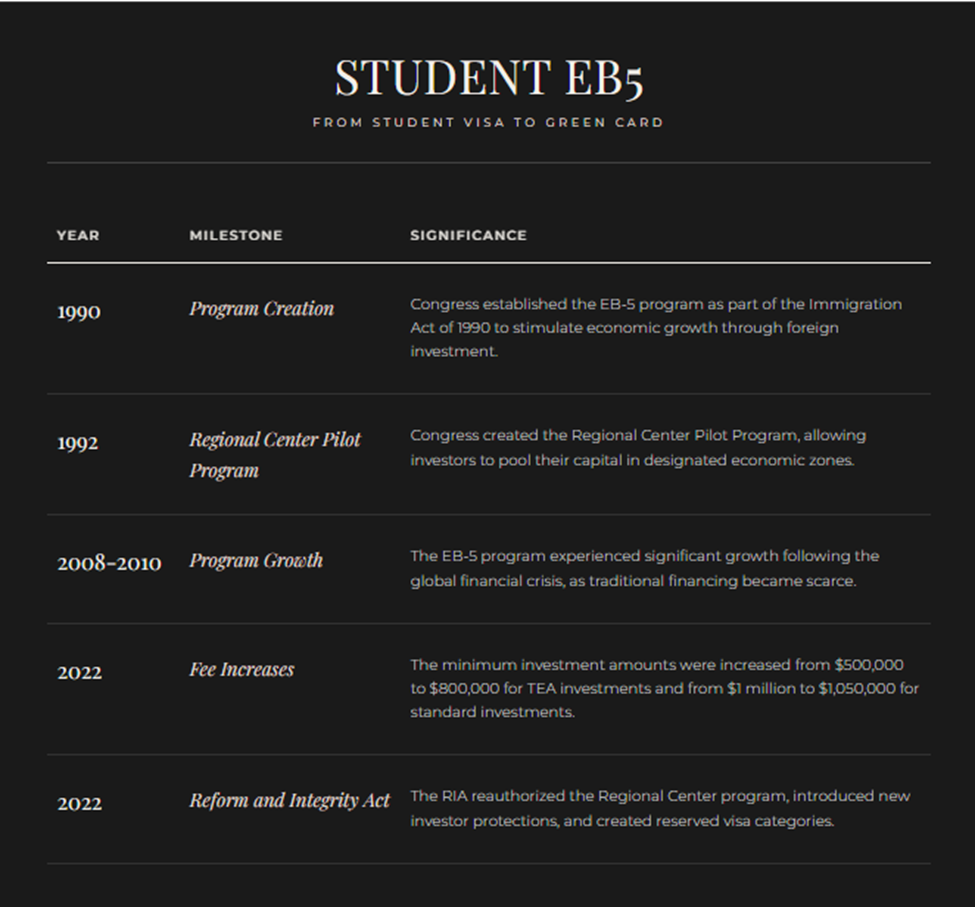
The program has grown from processing only a few hundred applications annually in its early years to becoming one of the most sought-after investment immigration programs in the world.
What are the Key Requirements for EB-5 Investors?
To qualify for the EB-5 program, investors must satisfy numerous requirements. These requirements are designed to ensure that the program achieves its economic objectives while maintaining the integrity of the U.S. immigration system.
Investment Amount Requirements
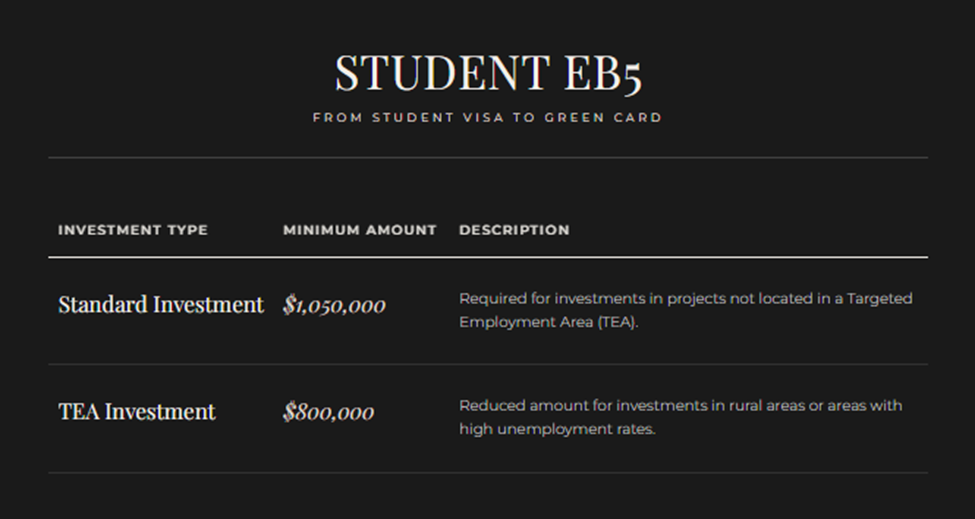
The investment amounts are subject to periodic adjustments based on inflation (this was introduced by the RIA). Investors should be aware that these amounts will most likely increase, which makes timely action advantageous when considering the program.
Job Creation Requirement
A fundamental requirement for the EB-5 program is that each investment must create at least 10 full-time jobs for qualifying U.S. workers. These jobs must be created within two years of the investor's admission to the United States as a conditional permanent resident. The definition of qualifying employees is very specific. These employees must be U.S. citizens or lawful permanent residents. The investor and their family cannot be counted toward this job creation requirement.
Investors can count direct and indirect jobs for investments made through regional centers. This is one of the primary advantages of the passive regional center model as it allows investors to meet the job creation requirement more easily through economic modeling.
Lawful Source of Funds Documentation
The most difficult and scrutinized aspect of the EB-5 application is the documentation of the lawful source of funds. Investors must provide comprehensive evidence demonstrating that their investment capital was obtained through legitimate means. Use our Source of Funds Calculator to plan your funding strategy. Acceptable sources of funds include:
• Employment income
• Business ownership
• Investment returns
• Real estate sales
• Inheritance
• Gifts
• Loans
The documentation requirements are extensive and usually include tax returns, bank statements, employment contracts, business records, property deeds and other financial documents spanning several years. Many investors find this aspect of the application process to be the most challenging. For H-1B professionals considering EB-5, proper financial planning is essential.
What is the At-Risk Requirement?
The EB-5 program requires that invested capital be placed "at risk" for the purpose of generating a return. This does not mean the investment must be risky! It means that the investment cannot be guaranteed or protected from loss.
The EB-5 Process Step by Step
Step 1: Select an Investment Project
The first critical step is selecting an appropriate EB-5 investment project. Investors have two options:
Direct Investment: The investor creates or invests directly in a new commercial enterprise and takes an active role in the entity's management.
Regional Center Investment: The investor places their capital with a USCIS-designated regional center. The regional center pools funds from multiple investors and manages the investment on their behalf.
The most popular route for EB-5 investors is the regional center model due to its advantages in job creation counting and the passive nature of the investment.
When evaluating potential projects, investors should consider:
• The track record of the regional center and history of successful petitions
• The business plan
• The security of the investment structure
• Whether the project has received exemplar approval (I-956F approval)
• The projected timeline for completion and capital return
Step 2: Filing Form I-526E (Regional Center) or I-526 (Direct Investment)
Once the investment is made, the investor's immigration attorney files Form I-526E with U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services. This petition serves as the formal application for EB-5 classification. Processing times for I-526E petitions vary depending on the type of project and current USCIS workload. Rural projects benefit from priority processing with some approvals occurring in as little as four months.
Step 3: Obtaining Conditional Permanent Residency
After approval of the I-526E petition, the investor and their qualifying family members become eligible for CPR (conditional permanent resident) status.
If the investor is already in the United States, they can concurrently file:
• Their I-485 to adjust their status without leaving the country
• Their EAD (employment authorization document) so they can work freely
• Their AP (advance parole) so they can travel freely
If they're outside of the United States, investors must complete consular processing at a U.S. embassy or consulate in their home country.
The conditional green card is valid for two years and provides nearly all the benefits of permanent residency.
Step 4: Remove Conditions (Form I-829)
Investors must file Form I-829 within the 90-day period before the two-year conditional residency period expires. Form I-829 is a petition by the investor to remove conditions on permanent resident status.
This petition requires the investor to demonstrate that:
• The investment has been sustained throughout the conditional period
• The required jobs have been created or will be created within a reasonable time
• The investor continues to meet all EB-5 requirements
Upon approval of the I-829 petition, the conditions are removed and the investor and their family receive a permanent 10-year green card which can be renewed indefinitely.
Step 5: Pathway to Citizenship
After maintaining permanent resident status for five years, EB-5 investors become eligible to apply for U.S. citizenship through naturalization. This process usually involves:
• Demonstrating continuous residence in the United States
• Passing an English language test
• Passing a civics test on U.S. history and government
• Taking the Oath of Allegiance
What is the Difference Between Rural and Urban Projects? And What is a Targeted Employment Area?
The EB-5 Reform and Integrity Act of 2022 placed a significant emphasis on investments in targeted employment areas and created a system of reserved visas. Use our TEA Project Explorer to find qualifying projects.
A Targeted Employment Area (TEA) is either:
• A rural area (outside a metropolitan statistical area or outside the boundary of any city or town with a population of 20,000 or more)
• A high unemployment area (an area that has experienced unemployment of at least 150% of the national average rate)
Investments in targeted employment areas qualify for the reduced threshold of $800,000 compared to $1,050,000 for non-TEA projects.
What are the Advantages of Rural EB-5 Projects?
Rural EB-5 projects have emerged as particularly attractive options for investors due to the following key advantages:

Urban TEA projects also offer the reduced $800,000 investment amount but receive a smaller visa set-aside (10% of annual visas) and do not benefit from priority processing. Processing times for urban TEA projects tend to be longer and range from 18-24 months or more.
The Reform and Integrity Act of 2022 and What is Grandfathering?
The passage of the EB-5 Reform and Integrity Act in March 2022 marked the most significant overhaul of the program since its creation. The RIA introduced numerous changes designed to protect investors and enhance program integrity.
One of the most important investor protections introduced by the Reform and Integrity Act is the requirement for third-party fund administration. New Commercial Enterprises must now retain an independent fund administrator to oversee the management of EB-5 capital.

Current Immigration Landscape and the EB-5 Advantage
The current U.S. immigration landscape has created unprecedented interest in the EB-5 program. Several factors have contributed to the EB-5 tsunami:
The H-1B program is under fire and has undergone significant changes. New fee structures and a more strenuous selection process has created uncertainty for employers and visa holders. The EB-5 program offers a path to permanent residency that does not depend on employer sponsorship. Learn more about why H-1B holders are switching to EB-5.
Concurrent filing for individuals already in the United States on valid non-immigrant visas allows filing for adjustment of status concurrently with the I-526E petition. This provides significant advantages to F-1 student visa holders because it allows investors to:
• Obtain work authorization while their petition is pending
• Receive travel authorization to travel internationally
• Maintain legal status in the United States throughout the process
EB-5 vs. Proposed Trump Gold Card Comparison

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is a green card and how does it differ from other residency permits?
A green card grants the holder lawful permanent resident status in the United States and allows the holder to live and work permanently in the United States, travel freely in and out of the country, and eventually apply for U.S. citizenship. Temporary visas have limitations that don't allow the holder to freely work, travel, or live how they may want.
Q2: What is the difference between a conditional green card and a permanent green card?
EB-5 investors initially receive a conditional green card which is valid for two years. This conditional status requires the investor to demonstrate that they have fulfilled all program requirements before the conditions can be removed. The conditional green card provides all the same rights and privileges as a permanent green card—the only difference is the requirement to file Form I-829 to remove the conditions. Once the I-829 petition is approved, the investor receives a permanent 10-year green card which can be renewed every 10 years.
Q3: How long does the entire EB-5 process take from start to finish?
The timeline for the EB-5 process varies and depends on several factors including the type of project, the investor's country of origin, and current USCIS processing times:
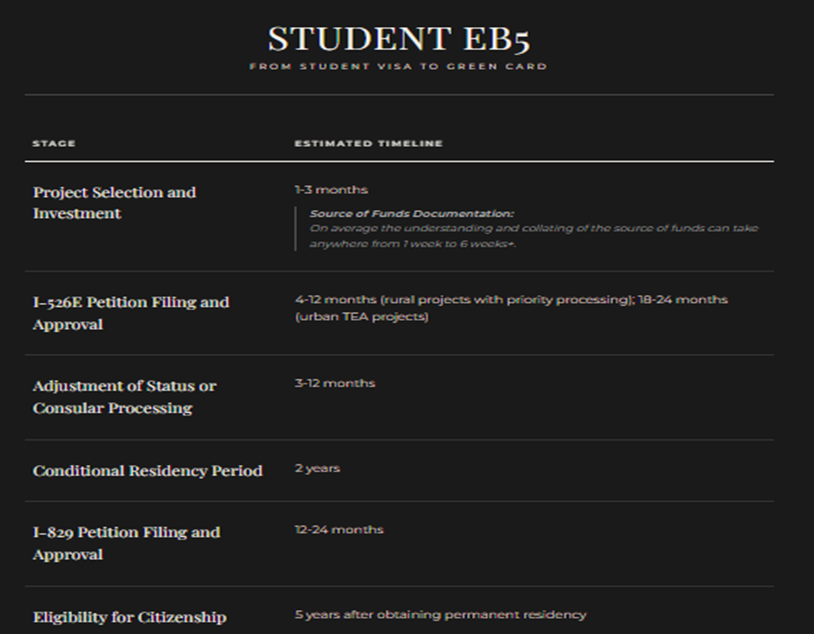
Priority processing for rural projects can see investors receive I-526E petition approvals in as little as four months.
Q4: Is my $800,000 investment a donation or can I get my money back?
The EB-5 investment is not a donation—it is a genuine business investment. While the capital must be "at risk," that does not mean the project must be risky. The timeline and terms for capital return may vary by project and are typically outlined in a project's offering documents. Some projects offer exit strategies as early as three to five years after the investment is made.
Q5: Do EB-5 projects pay dividends or interest on the investment?
Investment returns vary significantly by project. Some projects offer annual dividends or preferred returns to investors while others do not provide any returns until the investment is exited. The return structure depends on the project's business model and financial projections.
Q6: What is the difference between debt and equity EB-5 projects?
EB-5 investments are typically structured as either debt or equity:
Debt Structure: The EB-5 capital is loaned to the project and investors receive a fixed interest rate. This structure often provides more predictable returns but may offer lower overall returns.
Equity Structure: The EB-5 capital is invested as equity in the project and investors share in the profits or losses of the enterprise. This structure may offer higher potential returns but carries more risk for the investor.
Q7: What is I-956F approval and why is it important?
Form I-956F is filed by a regional center to seek USCIS approval of their EB-5 projects before investors file their individual petitions. When a project receives I-956F approval (sometimes called exemplar approval), it means that USCIS has reviewed and approved of the project's business plan, economic study, and job creation methodology. Investing in a project with I-956F approval significantly reduces the risk of petition denial due to project-related issues.
Q8: How do I evaluate the quality of an EB-5 project?
When evaluating an EB-5 project, investors should consider the following:
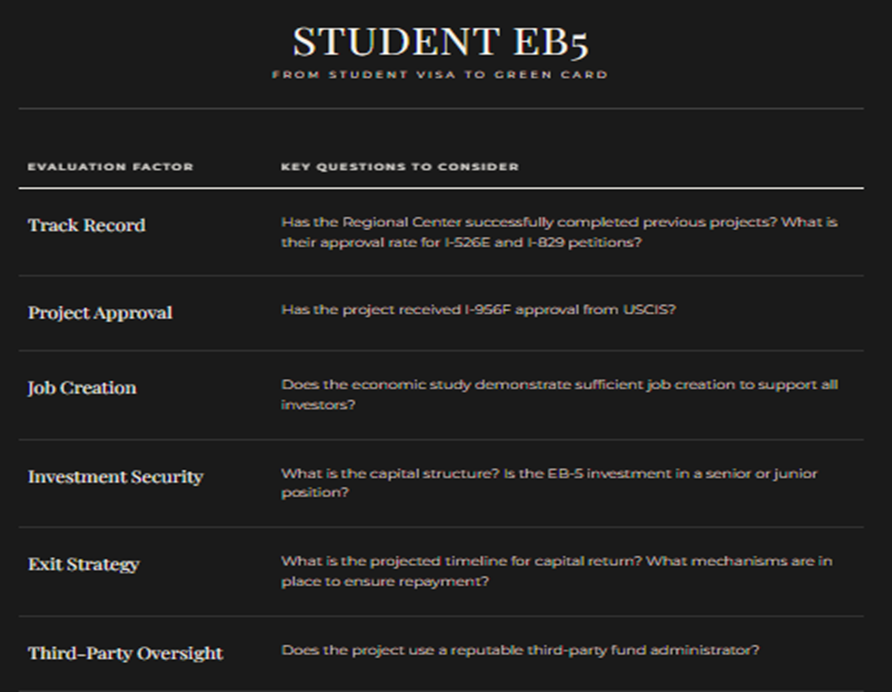
Q9: What happens when the EB-5 program authorization expires in 2027?
The regional center program is currently authorized through September 30, 2027. Its future will depend on congressional actions. Investors who file their petitions before September 30, 2026 will protect themselves from any changes and be protected by grandfathering provisions. Learn more about the critical 2026 and 2027 deadlines and track the countdown with our Grandfathering Countdown Timer.
Conclusion
The EB-5 immigrant investor program represents one of the most established and reliable pathways to U.S. permanent residency for foreign investors. With its clear legal framework, family inclusion benefits, and potential for capital return, it provides a compelling option for those who have the means to make a significant investment in the American economy.
The reforms introduced by the EB-5 Reform and Integrity Act of 2022 have solidified investor protections and created new opportunities through reserved visa categories for rural and high unemployment areas. Rural projects have benefited the most due to the significant advantages offered through priority processing and larger visa allocation.
With proper preparation and due diligence in project selection, the EB-5 program can serve as a transformative opportunity for investors and their families to build a new life in the United States.
---
Ready to learn more about the EB-5 program? Contact StudentEB5 at [www.studenteb5.com](https://www.studenteb5.com) for a free consultation.
References
• U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services. (2023, March 1). EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program. https://www.uscis.gov/working-in-the-united-states/permanent-workers/eb-5-immigrant-investor-program
• Congress.gov. (2025, June 23). Overview of the EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program. https://www.congress.gov/crs-product/IF13040
• U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services. (n.d.). EB-5 Immigrant Investor Program – Family Benefits. https://www.uscis.gov/working-in-the-united-states/permanent-workers/eb-5-immigrant-investor-program
• U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services. (2022, July 11). EB-5 Reform and Integrity Act of 2022. https://www.uscis.gov/working-in-the-united-states/permanent-workers/eb-5-reform-and-integrity-act-of-2022-updated-april-2022
The opinions expressed on this website are solely those of the author/presenter. The information provided is for general informational purposes only and should not be considered professional or legal advice. StudentEB5 and its contributors do not endorse or take responsibility for any actions taken based on the information presented here. Visitors are strongly advised to consult with qualified immigration attorneys and financial advisors before making any EB-5 investment decisions or taking any actions based on the content on this website.



